Hydroxypropyl Beta-Cyclodextrin as a Multifunctional Excipient for Downstream Processing and Formulation of Monoclonal Antibodies
Published January 27, 2026
Presented at the AAPS 2024 PharmaSci 360, October 20-23, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA.
Authors
Shiqi HONG
Biopharma Senior Scientist, Roquette Asia Pacific Pte Ltd, 138588 Singapore
Jiayi Huang
Biopharma Scientist, Roquette Asia Pacific Pte Ltd, 138588 Singapore
Hailong Zhang
Analytical Manager, R&D analysis, Roquette Asia Pacific Pte Ltd, 138588 Singapore
Tao Peng
BioPharma Research Manager, Roquette Asia Pacific Pte Ltd, 138588 Singapore
Keat Theng Chow
Pharmaceutical Research Manager, Pharmaceutical R&D, Roquette Asia Pacific Pte Ltd, 138588 Singapore
Rajeev GOKHALE
Head of Global Pharmaceutical Sciences, Roquette America Inc., Geneva, IL 60134, USA
Vinod Tuliani
VP & Head of Global Pharmaceutical Sciences, Roquette
Purpose
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized modern medicines in the fast-growing biopharmaceuticals sector. However, the inherent instability of protein molecules presents significant challenges in downstream processing, final formulation, and drug delivery [1]. For example, particle formation or protein aggregation can occur during unit operations such as ultrafiltration/diafiltration (UF/DF) [2]. Also, the inherent stability limitations of mAbs will require careful formulation.
Objectives
In this work, we investigated KLEPTOSE® HP, HPB and HPB-LB hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin (HPβCD) as a multifunctional excipient to reduce particle formation during UF/DF of different mAbs and in subsequent formulation. The stabilizing effect of KLEPTOSE® HPβCD was compared with polysorbates and their combinations as excipients in mAbs formulations were evaluated.
Methods
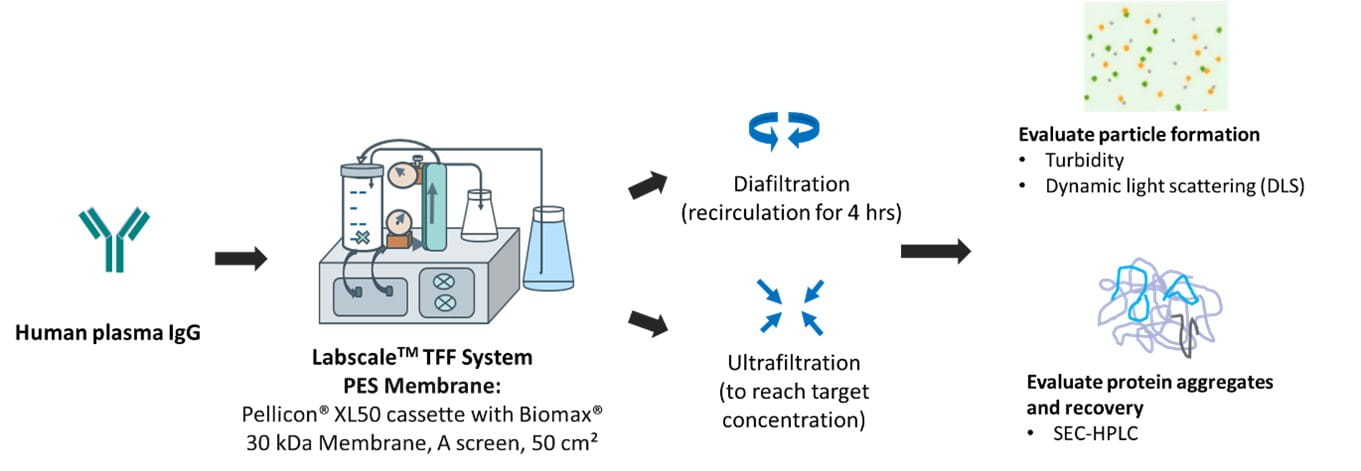
1. UF/DF study
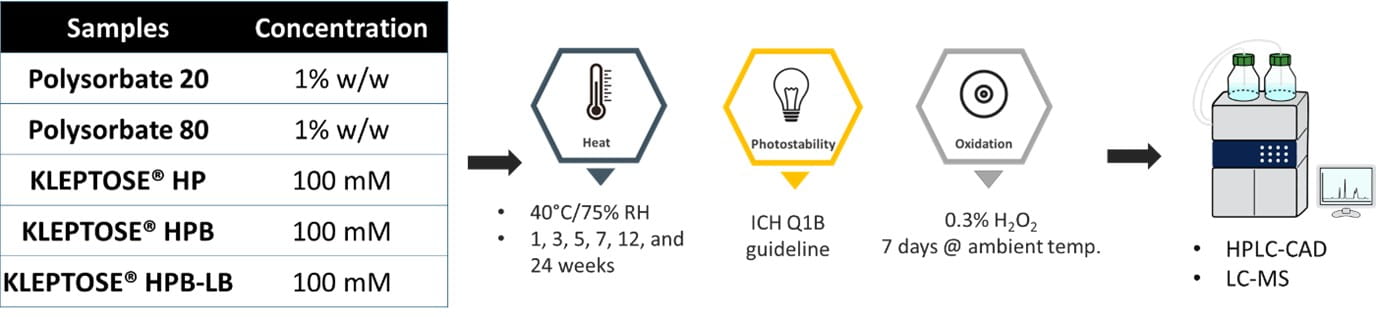
2. Force degradation studies of HPβCD (KLEPTOSE® HP, HPB, and HPB-LB) and polysorbates
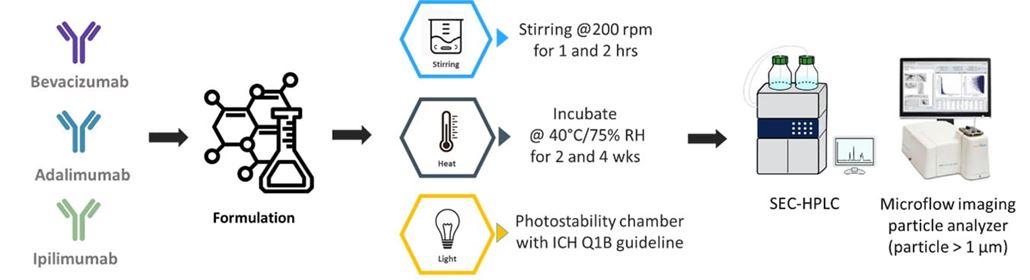
3. Antibody Formulation and Stability Studies
Results
Ultrafiltration/Diafiltration (UF/DF)
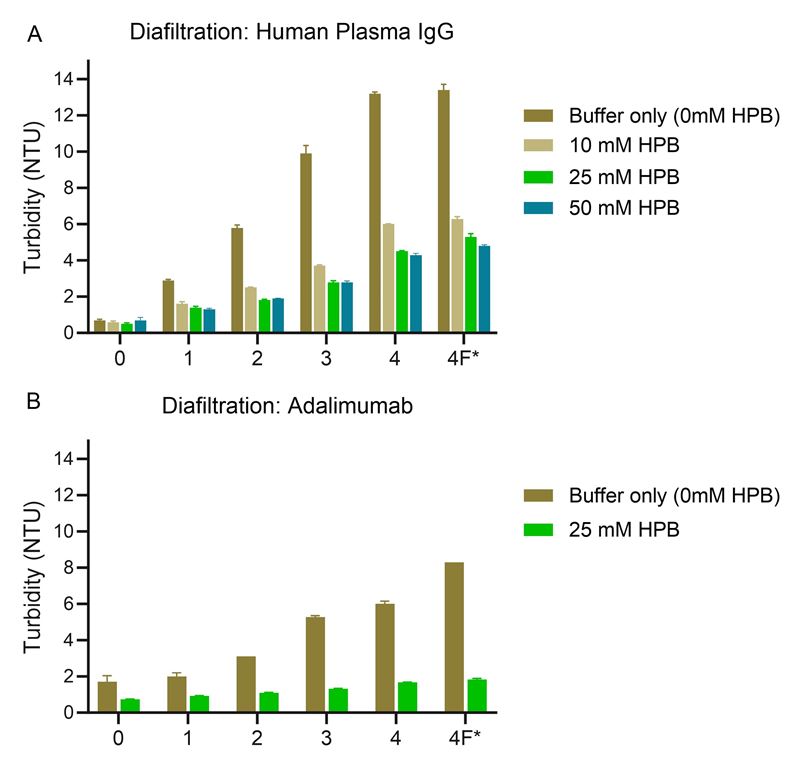
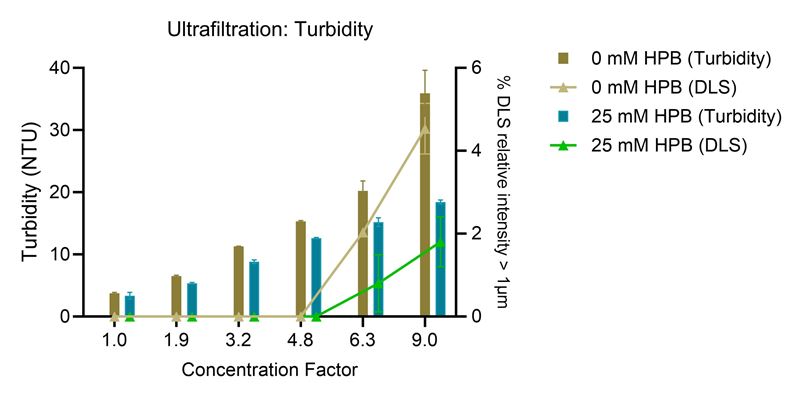
Ultrafiltration/diafiltration (UF/DF) processes are known to cause significant stresses to proteins, potentially leading to protein aggregation, particle formation and product losses. Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the efficacy of KLEPTOSE® HPB in mitigating UF/DF-induced particle formation in Human IgG plasma and adalimumab solutions:
- The addition of KLEPTOSE® HPB significantly reduced the rate of turbidity increase in both Human IgG plasma and adalimumab solutions.
- A lower relative intensity of larger particles in the presence of KLEPTOSE® HPB.
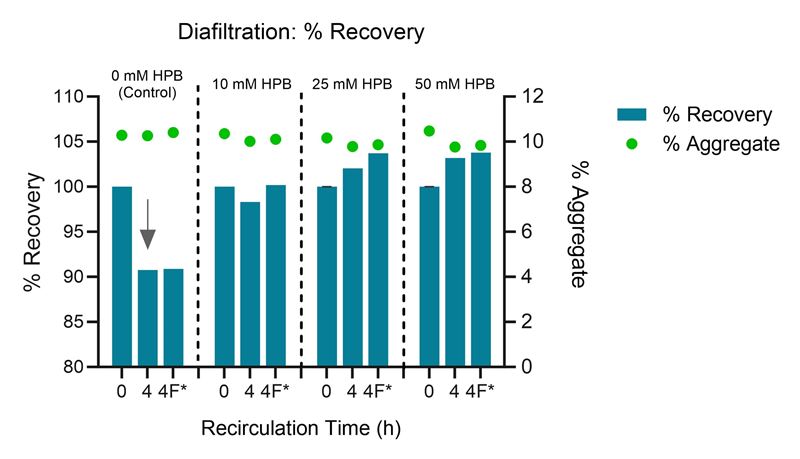
Furthermore, KLEPTOSE® HPB also greatly improved protein recovery of human plasma IgG solution as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 1. Turbidity of (A) 1 mg/mL human plasma IgG solution and (B) 2 mg/ml adalimumab with and without KLEPTOSE® HPB after UF/DF recirculation (n=3, mean ±SE). * 4F denotes final product recovery after flushing from membrane.
Figure 2. Turbidity and % DLS relative intensity of particles >1 μm after ultrafiltration of human plasma IgG solution from 10 to 90 mg/mL, (n=3, mean ±SE). Concentration factor = protein concentration/initial protein concentration.
Figure 3. Protein recovery and aggregate levels in 1 mg /mL human plasma IgG solution after diafiltration. *4F denotes final product recovery after flushing from membrane.
Forced degradation of HPβCD and polysorbates
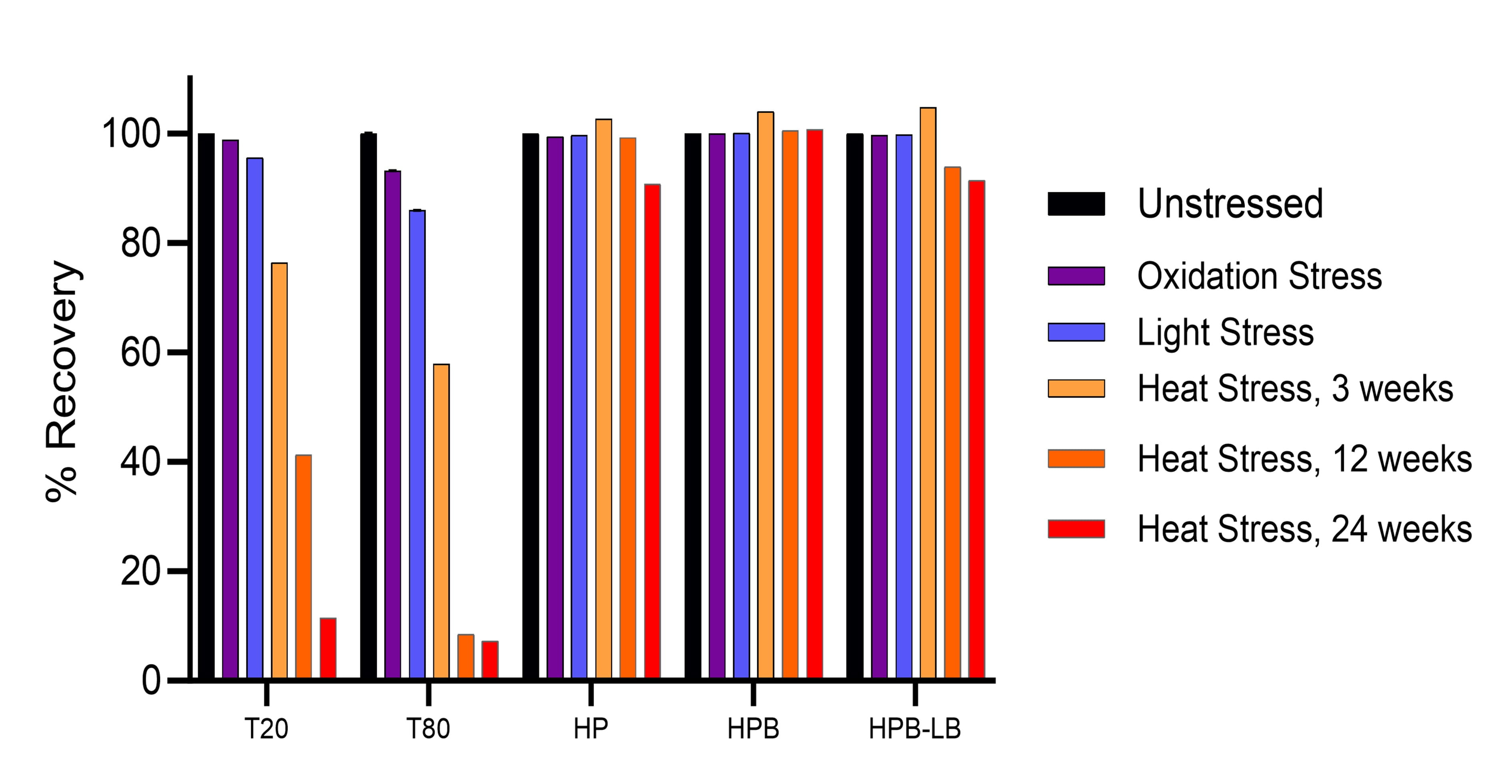
The chemical stability of KLEPTOSE® HPβCD is compared to that of polysorbates (PS) under various stress conditions. Figure 4 illustrates the stability of HPβCD and polysorbates (PS) under oxidative, light and heat stresses. The results indicate that:
- When subjected to heat stress, PS20 and PS80 undergo tremendous degradation, while KLEPTOSE® HPβCD maintained its stability.
- KLEPTOSE® HPβCD shows superior stability under light, and oxidation stresses than PS20 and PS80.
Figure 4. Stability study of polysorbates and KLEPTOSE® HPβCD under oxidative, light and heat stresses.
Antibody Formulation and Stability Studies
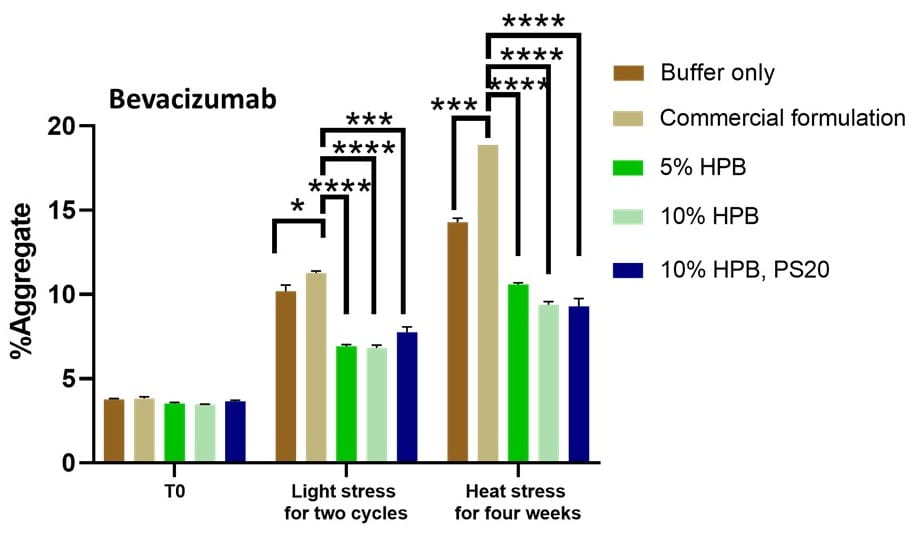
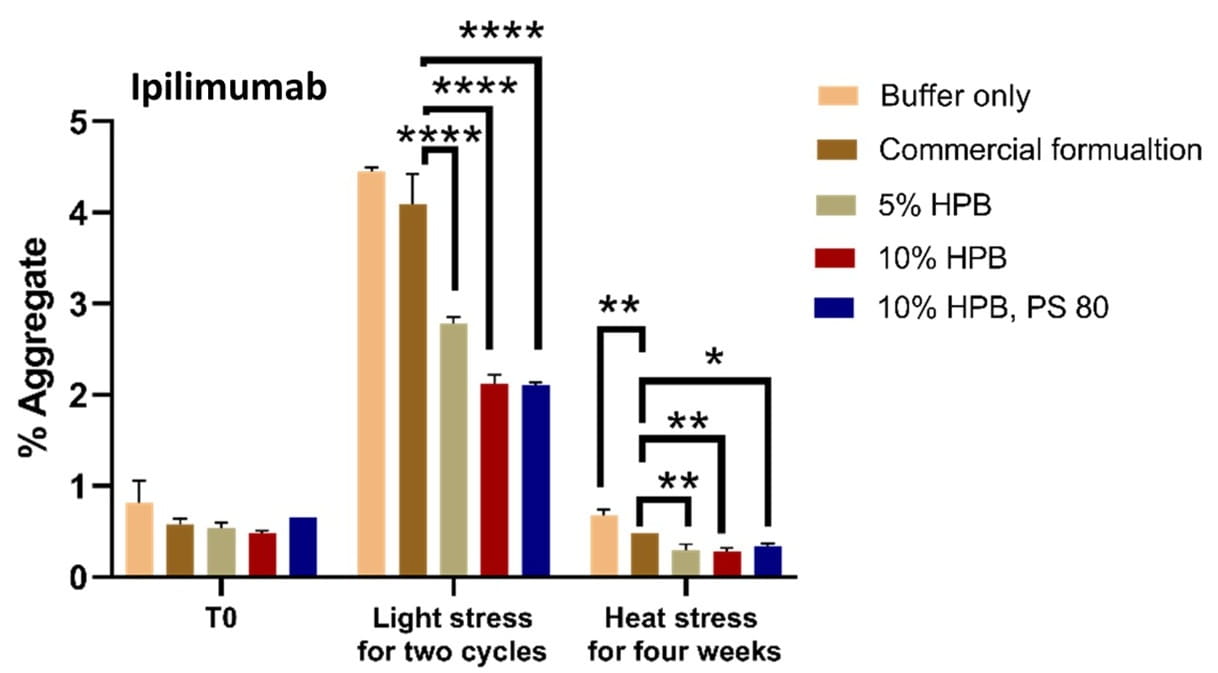
Figures 5 and 6 illustrate the levels of aggregates obtained under light and heat stresses for bevacizumab and Ipilimumab. The data indicate that KLEPTOSE® HPβCD, either alone, or combination with polysorbates, enhanced the stability of various mAbs by reducing protein aggregation under these various conditions.
Figure 5. Bevacizumab aggregation levels under light and heat stresses. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA compared to the commercial formulation.
Figure 6. Ipilimumab aggregation levels under light and heat stresses. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA compared to the commercial formulation.
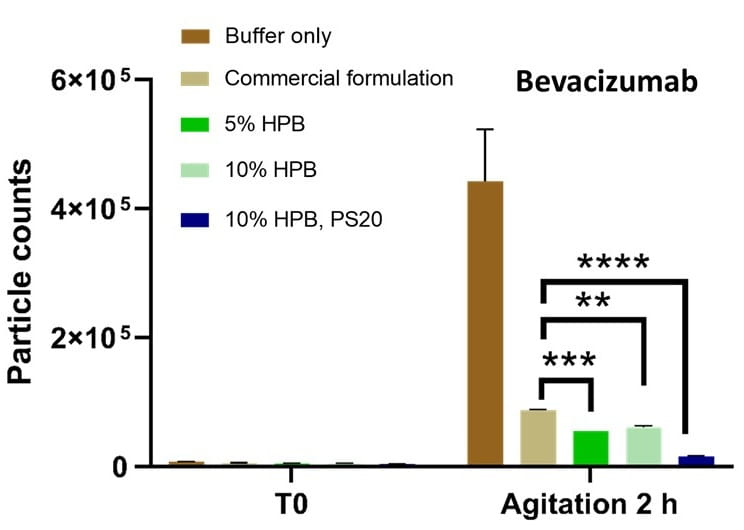
Figure 7 presents the particle formation under agitation stress for bevacizumab formulations. It is clearly demonstrated here that KLEPTOSE® HPβCD alone, or combination with polysorbates, helps reduce particle formation caused by agitation stress.
Figure 7. Particle formation with bevacizumab in different formulations under agitation stresses. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA compared to the commercial formulation.
The efficacy of KLEPTOSE® HPβCD with and without polysorbate in reducing mAbs aggregation and particle formation is summarized in tables 1 and 2.
Table 1. Effectiveness of different formulations on reducing aggregation of three mAbs under stresses. Numbers of + represent the degree of effectiveness compared to samples formulated in buffer only.
| Type of stress | Formulation | Effectiveness in reducing aggregation | ||
| Bevacizumab | Adalimumab | Ipilimumab | ||
| Light stress | HPB | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| HPB+Polysorbate | +++ | +++ | +++ | |
| Heat stress | HPB | +++ | No change | + |
| HPB+Polysorbate | +++ | No change | + | |
Table 2. Effectiveness of different formulation on reducing particle formation of three mAbs under stresses. Numbers of + represent the degree of effectiveness compared to samples formulated in buffer only.
| Type of stress | Formulation | Effectiveness in reducing particle formation | |
| Bevacizumab | Adalimumab | ||
| Light stress | HPB | +++ | +++ |
| HPB+Polysorbate | +++ | ++ | |
| Heat stress | HPB | ++ | + |
| HPB+Polysorbate | ++ | + | |
| Agitation | HPB | +++ | +++ |
| HPB+Polysorbate | ++++ | ++++ | |
Conclusion
This study has demonstrated the utility of KLEPTOSE® HPβCD as a versatile excipient for UF/DF process and in subsequent protein formulation:
- Our findings reveal that HPβCD exhibits excellent chemical stability under various stress conditions, highlighting its potential as a promising excipient for biotherapeutic downstream processing and formulation.
- KLEPTOSE® HPβCD enhances protein recovery and minimizes particle formation during ultrafiltration and diafiltration.
- It effectively reduces protein aggregation under heat and light stress in several monoclonal antibody formulations, as shown in stability studies.
- Notably, when combined with polysorbates, KLEPTOSE® HPβCD significantly decreases antibody aggregation and subvisible particle counts under multiple stressors, outperforming commercial formulations.
References
1.Castañeda Ruiz, A. J.; Shetab Boushehri, M. A.; Phan, T.; Carle, S.; Garidel, P.; Buske, J.; Lamprecht, A., Alternative Excipients for Protein Stabilization in Protein Therapeutics: Overcoming the Limitations of Polysorbates. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14 (12), 2575. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122575
2.Dwivedi, M.; Blech, M.; Presser, I.; Garidel, P., Polysorbate degradation in biotherapeutic formulations: identification and discussion of current root causes. International journal of pharmaceutics 2018, 552 (1-2), 422-436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.10.008