Mitigating Particle Formation During Ultrafiltration/Diafiltration of Biologics with KLEPTOSE® HPβCD (Hydroxypropyl Beta-Cyclodextrin)
INTRODUCTION
Ultrafiltration/diafiltration (UF/DF) is an integral part of every biotherapeutic downstream process. A typical UF/DF process requires several passes through the pump and the membrane cassette, often taking several hours for completion. During this time, proteins are exposed to several physical stresses, forming higher order aggregates and particulates.1 Interfacial interaction is reportedly one of the causes of particle formation during UF/DF.2 Although polysorbates are one of the most used surfactants to prevent interfacial stresses, they are not applicable in UF/DF. Adsorption of polysorbates on the membrane or the formation of micelles bigger than the molecular weight cutoff of the membrane will result in varying concentrations and membrane clogging during the UF/DF process.
In this work, we have explored the use of hydroxypropyl ß-cyclodextrin (KLEPTOSE® HPB) as a non-micellar additive in UF/DF application. It is known to possess surface activity and has been shown to protect protein against interfacial stresses.3 Two aspects were investigated: (i) the permeability of KLEPTOSE® HPB in commonly used UF/DF membrane types and (ii) the effect of KLEPTOSE® HPB on reducing
particle formation during UF/DF of human plasma IgG and adalimumab solutions.
EFFECT OF MEMBRANE TYPE ON THE PERMEABILITY OF KLEPTOSE® HPB

| KLEPTOSE HPB Concentration (mM) | ||||||||
|
(A) Regenarated cellulose membrane |
(B) Polyethersulfone membrane |
|||||||
| Input (1) | 200 | 100 | 50 | 25 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 25 |
| Retentate (2) | 209 | 119 | 75 | 51 | 200 | 98 | 51 | 25 |
| Permeate (3) | 82 | 25 | 13 | 5 | 200 | 99 | 50 | 25 |
Table 1. Concentration of KLEPTOSE® HPB in retentate and permeate in (A) regenerated cellulose and (B) polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane after centrifugation.
Varying concentrations of KLEPTOSE® HPB in the retentate and permeate were observed in regenerated cellulose membrane after centrifugation (Table 1A). This indicated that the regenerated cellulose membrane was retaining KLEPTOSE® HPB during ultrafiltration. In contrast, KLEPTOSE® HPB concentrations remained constant in polyethersulfone (PES) membrane for all four concentrations (Table 1B).
This indicated that KLEPTOSE® HPB was able to pass through PES membrane freely.
- KLEPTOSE® HPB was not retained in PES membrane, which is the most used membrane type for commercial UF/DF cassettes.
PERMEABILITY OF KLEPTOSE® HPB IN TFF SETUP
Permeability of KLEPTOSE® HPB at 50 mM was also evaluated in a tangential flow filtration (TFF) setup using LabscaleTM TFF System with Pellicon® XL50 cassette with Biomax® (PES) Membrane, A screen, 50 cm² from Merck KGaA.

Figure 1. Concentration of KLEPTOSE® HPB in retentate and permeate after (A) diafiltration and (B) ultrafiltration.
In a TFF setup, the permeability of KLEPTOSE® HPB during UF/DF was evaluated. Concentration of KLEPTOSE® HPB was maintained throughout at 50 mM at various locations in both the diafiltration and ultrafiltration setup (Figure 1).
- This demonstrated that KLEPTOSE® HPB does not get retained on PES membrane during UF/DF and is a suitable additive for use in UF/DF of biologics.
EFFECT OF KLEPTOSE® HPB ON PARTICLE FORMATION DURING UF/DF
Using the same TFF setup, UF/DF experiments of human plasma IgG and adalimumab in the presence of different concentrations of KLEPTOSE® HPB were conducted. In the diafiltration setup, both the retentate and permeate were recirculated for four hours to mimic the duration of a typical diafiltration process.

Figure 2. Diafiltration and ultrafiltration of protein solution in different concentrations of KLEPTOSE® HPB in a tangential flow filtration (TFF) setup.
KLEPTOSE® HPB REDUCED UF/DF-INDUCED PARTICLE FORMATION

Figure 3. Particle formation in 1 mg /mL human plasma IgG solution after UF/DF recirculation. (A) Turbidity and (B) DLS relative intensity >0.1μm of human plasma IgG with and without KLEPTOSE® HPB (n=3, mean ±SE). * 4F denotes final product recovery after flushing from membrane.
Presence of KLEPTOSE® HPB modulated the rate of turbidity increase in human plasma IgG solution (Figure 3A). Turbidity of sample was reduced by more than two times in the presence of just 10 mM of KLEPTOSE® HPB. DLS data also showed that KLEPTOSE® HPB lowered the % relative intensity of larger particles (> 0.1 μm) compared to control sample (i.e., without KLEPTOSE® HPB) (Figure 3B).
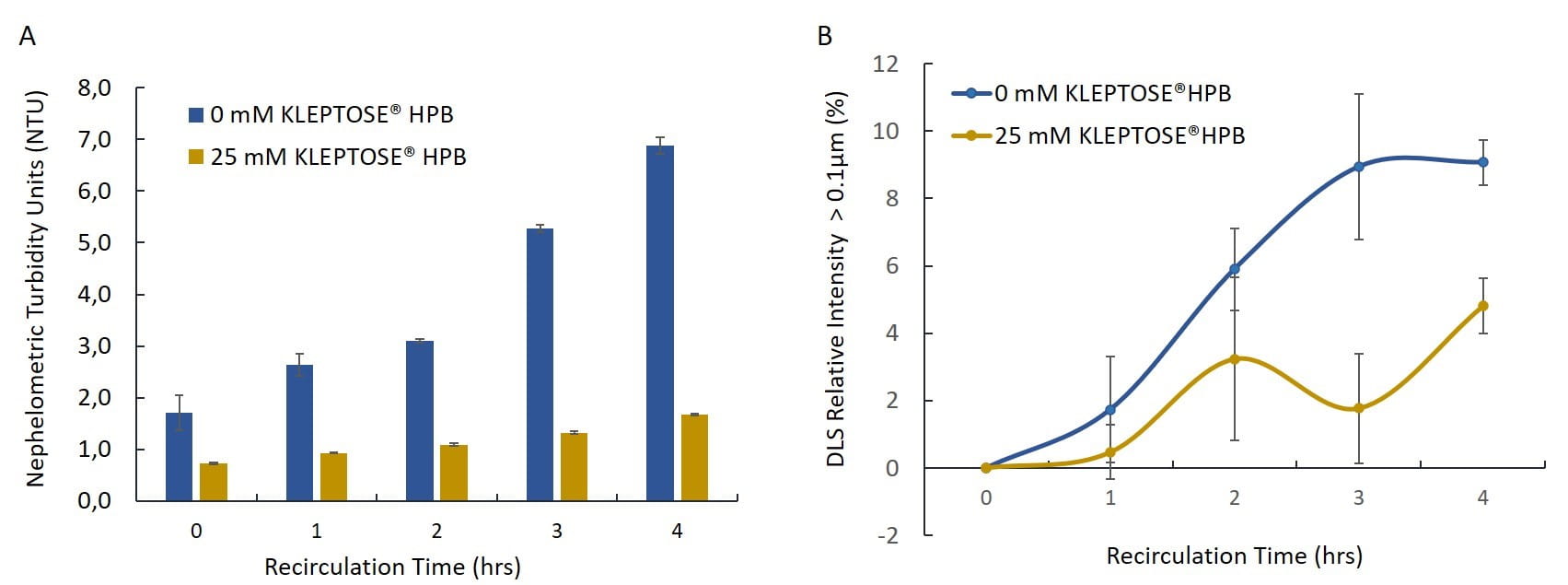 Figure 4. Particle formation in 2 mg/mL adalimumab solution during UF/DF recirculation. (A) Turbidity and (B) DLS relative intensity >0.1μm of adalimumab with and without KLEPTOSE® HPB (n=3, mean ±SE).
Figure 4. Particle formation in 2 mg/mL adalimumab solution during UF/DF recirculation. (A) Turbidity and (B) DLS relative intensity >0.1μm of adalimumab with and without KLEPTOSE® HPB (n=3, mean ±SE).
The addition of 25 mM KLEPTOSE® HPB significantly reduced the rate of turbidity increase in adalimumab solution (Figure 4A). The final turbidity was more than four times lower in sample with KLEPTOSE® HPB compared to the control sample. A lower relative intensity of larger particles (>0.1 µm) in the presence of KLEPTOSE® HPB (Figure 4B) was also observed.
- The results indicated that KLEPTOSE® HPB was effective in reducing UF/DF-induced particle formation in both human plasma IgG and adalimumab solutions.
KLEPTOSE® HPB IMPROVED PROTEIN RECOVERY DURING DIAFILTRATION

Figure 5. Protein recovery and aggregate levels in 1 mg /mL human plasma IgG solution after diafiltration. *4F denotes final product recovery after flushing from membrane.
Protein recovery and aggregate levels during the diafiltration recirculation process were monitored. Adalimumab is relatively stable. As such, aggregate levels and recovery were not significantly impacted during the recirculation process (Results not shown). However, in the case of human plasma IgG, about 10 % protein loss was observed in the control sample (i.e., without KLEPTOSE® HPB). In contrast, all samples containing KLEPTOSE® HPB maintained around 100 % protein recovery at the end of four hours.
KLEPTOSE® HPB REDUCED PARTICLE FORMATION DURING ULTRAFILTRATION

Figure 6.Turbidity and % DLS relative intensity of particles >1 μm after ultrafiltration of human plasma IgG solution from 10 to 90 mg/mL, (n=3, mean ±SE). Concentration factor = protein concentration/ initial protein concentration.
The turbidity and formation of particles in human plasma IgG increased substantially as protein concentration increased during ultrafiltration (Figure 6). As shown more pronouncedly at higher concentration factors, KLEPTOSE® HPB substantially lowered the turbidity and reduced the formation of larger particles (> 1 micron) in human plasma IgG.
- This indicates that the addition of KLEPTOSE® HPB can help reduce the formation of particles during ultrafiltration.
KLEPTOSE® HPB EFFECTIVELY REDUCED AGITATION-INDUCED PARTICLE FORMATION

Figure 7. (A) Agitation study design and (B) Turbidity of 1 mg/mL human plasma IgG formulations at T0 and after agitation for 1 and 4 days (n=3, mean ±SE).
Effect of KLEPTOSE® HPB on reducing agitation-induced particle formation in final formulation was also studied (Figure 7A). Formulations containing KLEPTOSE® HPB showed approximately three times lower turbidity than in the control formulation (Figure 7B).
- KLEPTOSE® HPB was effective in reducing agitation-induced particle formation in protein formulations.
CONCLUSION
This study has demonstrated the suitability of KLEPTOSE® HPB, hydroxypropyl ß-cyclodextrin in UF/DF application. KLEPTOSE® HPB has been shown to reduce particle formation and improve protein recovery during UF/DF. In addition, its permeability in PES membrane allows its usage during UF/DF process without affecting its concentration. Lastly, KLEPTOSE® HPB has also shown to be useful in reducing agitation-induced particle formation in protein formulations. This multifunctional property makes KLEPTOSE® HPB a versatile excipient to be explored for biotherapeutic bioprocessing and formulation.
References
1. Vázquez-Rey, María & Lang, Dietmar. (2011). Aggregates in Monoclonal Antibody Manufacturing Processes. Biotechnology and bioengineering. 108. 1494-508.
https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23155
2. Callahan, D. J., Stanley, B., & Li, Y. (2014). Control of protein particle formation during ultrafiltration/diafiltration through interfacial protection. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 103(3), 862–869.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.23861
3. Serno T, Carpenter JF, Randolph TW, Winter G. Inhibition of agitation-induced aggregation of an IgG-antibody by hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin. J Pharm Sci. 2010 Mar;99(3):1193-206.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.21931